Are you looking to dine at a kosher restaurant but don’t know the right etiquette? Don’t worry, because we’ve got you covered! In this blog post, we’ll be discussing all of the dos and don’ts of eating out at a kosher restaurant. So grab a bite and get ready – it’s time to learn proper dining etiquette!
What Does Kosher Restaurant Means?

Kosher restaurants are establishments that offer traditional Jewish cuisine that adheres to stringent kosher laws. Etiquette for eating in a kosher restaurant is generally similar to any other establishment as dining etiquette is still based on a basic respect for the people and food you share.
However, there are some differences based on the specific laws observed in each establishment. It is always best to observe the host’s lead when entering a kosher restaurant and be aware of some important differences between this type of dining environment and a general non-kosher one.
They may require patrons to buy their food from certain establishments to ensure compliance with their specific Kosher regulations. All meat must be slaughtered according to Jewish law. Similarly, certain ingredients such as dairy products, seafood, and bread products that contain dairy will not be served together during a meal. Additionally, the kitchen staff may prepare meals under rabbinical supervision to further ensure compliance with religious dietary laws.
Dietary restrictions are not only followed in regards to what types of ingredients can or cannot be served together during a meal but also how they must be stored and prepared in order to maintain their Kosher status.
Meats should never come into contact with dairy products while cooking or after they have been cooked since this would make them non-kosher according to Jewish law. Additionally, plates used for one set of Kosher foods will not be used with another set meaning that two different sets of utensils must be used if both dairy and meat items will compose the meal being served at any point within an establishment’s Kosher guidelines.
Lastly, guests should always avoid cross-contamination by ensuring no dairy products ever come into contact with meats during the preparation or serving of a meal as many Kosher establishments adhere strictly to these guidelines out of respect for traditions followed within their religion as it pertains specifically when dining at these particular types of restaurants.
Types of Kosher Food

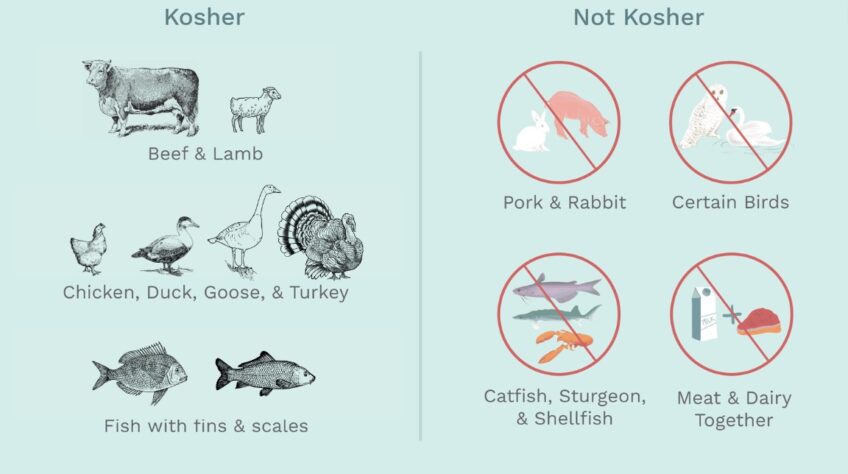
Kosher dishes are prepared according to Jewish law and religious supervision. Food is divided into three categories: meat (fleishig), dairy (milchig) and parve, which is a combination of the two but can generally just mean that the food does not contain any of the non-kosher animals or their by-products. It’s important to know the different types of kosher food before entering a kosher restaurant so you can make sure to order appropriately.
Meat dishes include all land animals that have cloven hooves and chew their cud, with some exceptions such as chickens from Ethiopia, camels from Arabia, ostriches from Africa, etc. This type of food is prepared in the kitchen according to Jewish dietary laws and then cooked using special utensils called fleishig and served on fleishig plates.
Dairy dishes include all milk products made from cows, goats or sheep but not foods made with mixtures of both dairy ingredients and non-dairy ingredients. Items such as ice cream sundaes or a dish of macaroni and cheese are considered milchigs because they contain both dairy ingredients (cream or cheese) and non-dairy ingredients (macaroni). These types of dishes are prepared in the kitchen according to Jewish dietary laws on separate dairy utensils called milchigs.
Parve dishes are made with neither dairy nor meat products but may include their by-products such as eggs, fish or honey. Dishes such as vegetable soups would be considered parve because they do not contain any prohibited substances at all. Utensils used for these types of dishes are called “parve” and must be handled accordingly within a restaurant setting.
Kosher Dietary Laws
Kosher dietary laws, take the health concern of maintaining a vegetarian diet one step further to provide nutritional and spiritual guidance. The Torah, the holy book of Jews, stipulates which foods can be consumed and how foods should be prepared. The most important concepts revolve around cleanliness, animal welfare and the separation between milk/dairy products and meat.
Kosher restaurants’ menus typically contain only certified ‘pareve’ food items without any dairy or meat elements. Additionally, ingredients with plant origins such as nuts must be confirmed as Kosher before being served in a kosher establishment.
In many cases, kosher diets require that food is not only prepared differently than non-kosher meals but also require that food is eaten separately – avoiding any combination of meat and dairy as much as possible. For example, a beef steak alongside vegetables cooked in butter would not be considered ok to eat in a kosher restaurant due to the combination of meat and milk derivatives.
Eating at a Kosher restaurant requires great attention to detail; diners should make sure they are familiar with all ingredients used in each dish they consume while always keeping an eye out for any potential mix of milk/dairy with other elements. Furthermore, many eating utensils such as plates or cutlery must also have been certified by a reliable source as acceptable for eating in accordance with Jewish dietary laws – to avoid unintentionally consuming non-kosher food products.
Table Manners at a Kosher Restaurant

When eating at a kosher restaurant, it’s important to have basic table manners and knowledge of the cultural etiquette associated with eating there.
- First, before beginning to eat, wash your hands in the traditional way by saying a blessing.
- Then, ask for any utensils you may need, such as forks or napkins.
- During the meal, be courteous and polite to anybody who is present and treat the food with respect.
- Finish eating on time without taking too long; leave room for others to get up if they wish to do so or finish eating their meal.
- Also, when ordering food, remember that most kosher restaurants will not serve any meat and dairy combinations as this is not permissible according to Jewish dietary law.
At the end of your meal be sure to pay attention and properly dispose of any wrappers or containers you may have been given by thanking those present. It is also polite to thank the staff for their service once you are finished with your meal at a kosher restaurant since there may not be many opportunities for tips in this context.
Finally, once you leave remember not to throw away anything that was provided by the restaurant since this would likely be seen as disrespectful according to many customs from this cultural background.
Ordering Food

When ordering food at a kosher restaurant, it’s important to understand the fundamental rules. Among those are the separation of meat and dairy and making sure no meat and dairy products have been mixed in food preparation.
When considering what to order, you will want to look for dishes that specifically indicate that they are made without any ingredients derived from animals, such as fish or eggs. Generally, any cuisine without meat is a safe bet. As for drinks, make sure there are no dairy or animal-derived ingredients used in any of the beverages offered. If you order alcoholic beverages, be sure there is no cream or gelatine in them.
Generally speaking, most traditional Jewish foods such as latkes and bagels do not contain any dairy products, but it’s still best to ask your server or read the menu carefully before ordering to make sure you’re getting something kosher-friendly.
If you have questions about a specific dish or drink, your server will be able to answer them for you—just ask! And if an item isn’t labeled with its kosher certification, it may be best not to order it because there may be hidden animal-derived ingredients that aren’t obvious on the menu.
Eating Rules

Eating at a Kosher restaurant can sometimes be a unique experience and require special protocols. Keeping in mind these etiquette tips will ensure you enjoy your visit and make sure that the restaurant remains in compliance with Jewish laws.
When planning to dine out at a Kosher restaurant, it is important to be aware of its basic guidelines. The most important rule is that no meat (including poultry) and dairy may be served together in the same meal. This means that even breads generally high in fat content, like bagels, cannot contain butter or margarine!
Also, care must be taken when ordering meals that involve animal products. All fish must have fins and scales for them to be recognized as Kosher. If a particular type of shellfish or seafood isn’t mentioned specifically on the menu, then chances are it isn’t allowed by law and should not be eaten. Additionally, there are some meats that are not regarded as kosher such as pork or rabbit-based dishes. It’s best to check ahead with the restaurant if you’re unsure about ordering something off of their menu.
In addition to being mindful of what can and cannot be ordered off of the menu, it is also important to adhere to standard table manners while dining at a kosher restaurant as with any other type of establishment. Be respectful of those around you by talking at an appropriate level, refraining from excessive movement or noise that could disrupt other guests, and tidying up after yourself by leaving things generally cleaner than when you arrived.
Kosher restaurants require careful observance but by following common sense etiquette tips they can make for especially enjoyable dining experiences regardless of religious beliefs!
Tips for Dining Out at a Kosher Restaurant

Eating in a kosher restaurant is a bit different from other dining experiences. To make sure you have the best experience and show proper respect for the restaurant’s policies and traditions, here are some tips for dining at a kosher restaurant:
- Check before you enter: Make sure you check with the restaurant beforehand to find out if there are any special observances that you need to be aware of during your stay. This could include entering through separate doors, leaving your shoes at the door, or even wearing a yarmulke.
- Respect dietary regulations: Kosher restaurants do not serve pork, shellfish, or dairy products. You will also find that meat dishes often come from animals slaughtered in accordance with Jewish laws. It is important to be aware of these restrictions when making your order.
- Be mindful of utensils: Utensils are often provided for customers at kosher restaurants so that guests do not mix milk and meats together on the same plate or use utensils for both milk and meat dishes. It is important to ask before you begin eating which utensil goes with which dish.
- Avoid talking about non-kosher food: As a guest at a kosher restaurant, it is prudent to avoid talking about non-kosher foods while in the establishment as this may be offensive to those who keep a strict diet according to Jewish law. When ordering food, refrain from making comparisons between what is served and non-kosher dishes available elsewhere.
In general, it’s best to err on the side of caution when visiting a kosher eatery; if unsure about something conduct related, feel free to ask questions of staff members so that everyone can enjoy their meals without worry!
FAQ
What is not allowed in kosher food?
1. Pork or shellfish – these are not considered kosher animals and so cannot be eaten.
2. Dairy and meat – these two food groups must be kept separate, so you cannot have milk and meat together in a dish.
3. Blood – this is also not considered kosher and so must be drained from meat before it is cooked.
Why KFC is not kosher?
KFC is not kosher because the company uses a variety of non-kosher ingredients in its food. These include things like pork fat, artificial flavorings, and non-kosher cheeses. Additionally, KFC’s cooking methods are not in line with kosher law. For example, the company uses fryers that are not kept strictly kosher and chicken that is not prepared in a kosher manner.
What happens if you break kosher?
If you break kosher, there are a few things that could happen. First, you may be breaking a religious law. Depending on how serious the violation is, you could be excommunicated from the Jewish community. Additionally, you may be subject to punishment from God. Finally, you may simply be making yourself ritually impure and unable to participate in certain religious ceremonies.
Why is beef kosher but not pork?
To be considered kosher, a food must meet certain criteria set forth in the Torah, the Jewish holy book. These include restrictions on which animals can be eaten and how they must be slaughtered. The requirements are designed to ensure that the animal is treated humanely and that its meat is clean and safe to eat.
Beef meets these criteria, but pork does not. Pigs are considered unclean animals in Judaism, so their meat is not kosher. In addition, pork products are often made from pig parts that would not be considered kosher even if the pig itself was allowed to be eaten. For example, pork sausage typically contains blood, which is not permitted under kosher law.
Conclusion
Visiting a kosher restaurant can be a wonderful and unique experience. While different restaurants have individualized rules, by following these broad tips you can feel confident that you are being respectful and honoring the values of the establishment.
- Remember to take the time to research what kind of food is served beforehand in order to ensure it fits within your dietary restrictions.
- Try asking friends who have visited a kosher restaurant before for suggestions.
- Lastly, make sure you observe all etiquette guidelines when dining at a Kosher restaurant and respect host’s wishes so everyone can enjoy their meals in peace and comfort.

